Introduction to Cancer Prevention
While tremendous progress combats many cancer types through earlier diagnosis and improved treatment options, prevention represents the ideal solution for avoiding this devastating disease. The adage “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” certainly holds true when considering cancer’s emotional, physical and financial toll. Cancer Prevention Research Thankfully robust emerging research identifies strategies and medical advances empowering people to reduce risk exposure, catch any cancerous changes early, and stop malignant spread before it progresses too far.
Lifestyle Approaches to Lower Cancer Risk
Large scale studies Quantify how certain daily choices significantly influence one’s lifetime cancer risk:
Read More: Lung Cancer Screening
- No smoking – Smoking remains the leading preventable cause of cancer-related deaths accounting for 1 in 3 diagnoses. Quitting brings immediate health dividends.
- Sun protection – Skin cancers are the most common malignancies, though minimizing UV exposure, avoiding tanning beds and regular screening curb incidents.
- Vaccination – Viruses cause several cancer types. HPV and HBV vaccines deter cervical, liver, throat, mouth, head/neck and anal cancers.
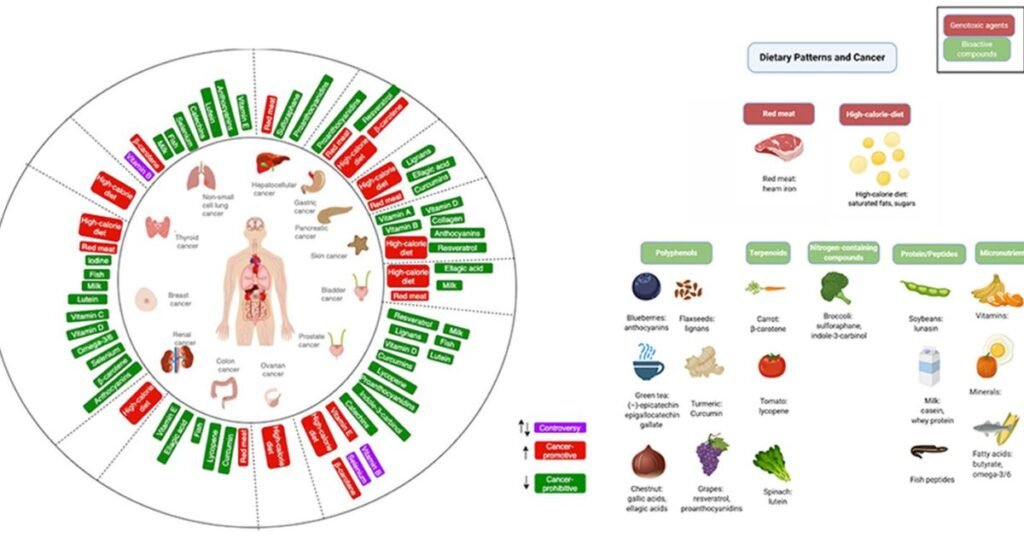
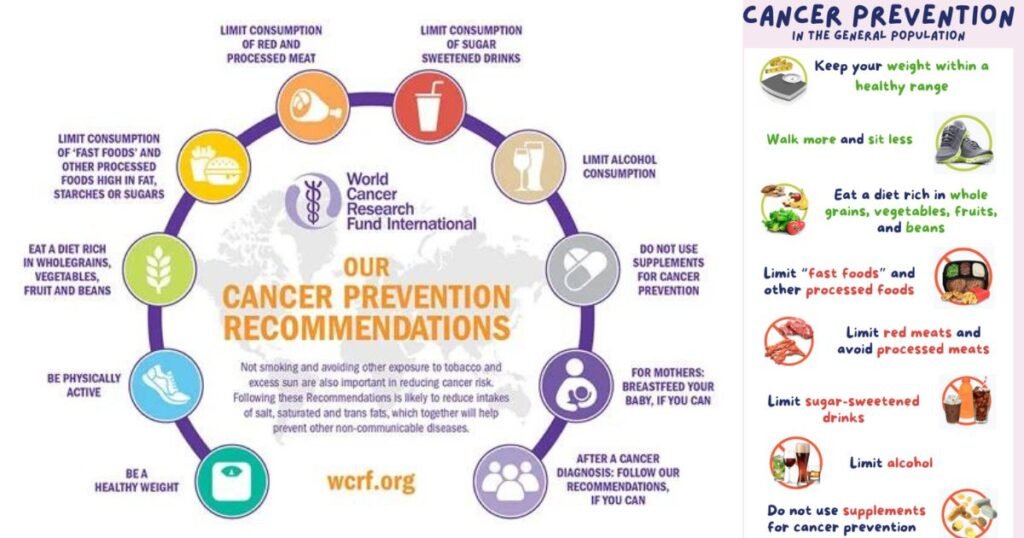
- Healthy diet – Diets high in fruits/vegetables, fiber and omega-3s while limiting red meats, processed foods, salt and added sugars deter development for many cancer sites.
- Physical activity – Regular exercise ideally 30 minutes daily lowers risks of several cancers by 18-28% through hormonal, immune and metabolic improvements.
- Avoid carcinogens – Limiting exposures to radiation, asbestos, benzene, arsenic and other carcinogens lowers avoidable risk.
- Alcohol moderation – Alcohol particularly impacts esophageal, liver, colorectal and breast cancer risk. Guidelines advise no more than 1 drink daily for women, 2 for men.
While cancer arises from many factors, individuals can substantially sway odds through healthy daily choices.
Emerging Medical Advances for Cancer Prevention
Beyond lifestyle measures, several medical advances expand prevention and early detection opportunities:
- Surgical prevention – Removing pre-cancerous tissues like colon polyps, DCIS breast lesions, and oral leukoplakias stops localized malignancy before spreading.
- Genetic testing – Identifying inherited mutations in BRCA or Lynch genes allows preventative mastectomy, ovary removal or colon excision.
- Cancer vaccines – Vaccines now exist preventing oncogenic strains of HPV, hepatitis B virus and H. Pylori bacterium avoiding associated cancer types.
- Early detection research – Advances like liquid biopsy sequencing and microbiome profiles may soon allow cancer screening from blood samples long before symptoms appear.
- Chemoprevention drugs – Certain risk subgroups may benefit from medications like aspirin, metformin and statins selectively preventing or delaying onset before progression.
On the horizon, next generation immunization, predictive diagnostics, prophylactic medications and gene therapies offer hope of neutralizing or eliminating early cancers before invasive potential.
Encouraging Advances in Cancer Treatment
Alongside prevention research, improved cancer treatments, immunotherapies and personalized care continue advancing survival and quality of life for those diagnosed allowing more to eventually die with instead of from cancer. Exciting gains demonstrate precisely targeted therapies destroy cancers previously quickly fatal. Macrosopic prevention, microscopic precision attacks, and immunologic checkpoints together expand survivors’ hopeful horizons.
Conclusion on Cancer Prevention
While cancer remains highly complex, increasing knowledge surrounding prevention, early detection, and treatment continues steadily progressing. Winding back the clock on cancer means applying lifestyle protective factors across populations alongside personalized medical approaches tailored to individuals’ genetic risks. Cancer Prevention Research As research insights accumulate and transform medical best practices, cancer incidence and mortality move favorably downward. Soon braces instead of biopsy may await those destined for better health through preventative care.
Cancer Prevention Research
Comprehensive guide on cancer prevention recommendations. This image provides a visual representation of essential tips and guidelines to reduce the risk of cancer. With a focus on promoting a healthy lifestyle, our product offers evidence-based strategies for individuals looking to take proactive steps towards preventing cancer. From dietary recommendations to exercise routines, this image serves as a valuable resource for anyone seeking to prioritize their health and well-being. Stay informed and empowered with our cancer prevention recommendations.

Read More: Cancer Prevention Research
FAQs:
What are the most preventable cancer types?
Lung cancer via smoking cessation, skin cancer through sun protection, cervical/oral cancer from HPV vaccination and hepatitis B prevention, and colon cancer with screening/polyp removal offer the Cancer Prevention Research most prevention potential.
Are foods that prevent cancer supported by research?
Yes large studies show diets high in fruits, vegetables, fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants reliably lower cancer risk while processed foods, excess salt, added sugar and red Cancer Prevention Research meats correlate with higher incidence.
Are there really anti-cancer vaccines?
Yes, vaccines now exist aimed at oncogenic viruses HPV and hepatitis B preventing almost 6% of cancers worldwide. Research continues on potential vaccination for breast and pancreatic cancers among others.
What are promising new advances for detecting cancer early?
Liquid biopsy sequencing blood for tumor DNA shows promise for screening where tissue biopsy is challenging. Cancer Prevention Research Breath analysis, microbiome shifts, and immune profiling offer additional early signals warranting further investigation.
Who should consider genetic testing to gauge inherited cancer risk?
Those with multiple family members diagnosed early or across generations with cancers like breast, ovarian, colon and pancreas may benefit from testing panels identifying mutations informing Cancer Prevention Research approaches.






