Introduction
Have you ever experienced a sudden or gradual weakening of your arms, making everyday tasks feel challenging or even impossible? Arm weakness can be a concerning symptom that may stem from various underlying conditions. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the potential causes, symptoms, and available treatments for arm weakness. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, you can take the necessary steps to address it effectively and improve your overall well-being.
Read More: Muscle Dysmorphia

Arm Weakness: A Closer Look
Arm weakness can manifest in different ways, affecting either one arm (right arm feels weak and heavy or why does my left arm feel weak all of a sudden) or both arms simultaneously (both arms feel heavy and weak). It can range from a mild sensation of heaviness or fatigue to complete loss of strength and mobility. Regardless of its severity, arm should never be ignored, as it may be an indicator of an underlying Health issue that requires prompt medical attention.
Causes of Arm Weakness
Arm weakness can result from a variety of factors, including musculoskeletal conditions, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular problems. Here are some common causes:
- Musculoskeletal Conditions:
- Injury or trauma to the muscles, tendons, or bones in the arm
- Arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis
- Repetitive strain injuries (RSI)
- Pinched nerves or nerve compression
- Neurological Disorders:
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson’s disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Cardiovascular Issues:
- Heart attack or myocardial infarction
- Peripheral artery disease
- Other Potential Causes:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Side effects of certain medications
- Autoimmune disorders
- Cancer (e.g., brain tumors, metastases)
It’s important to note that in some cases, the cause of weakness may be sudden (sudden weakness in both arms or sudden arm), Health while in other instances, it may develop gradually over time (why do my arms suddenly feel heavy and weak).
Arm Weakness Symptoms
While arm weakness itself is a symptom, it can be accompanied by other signs and symptoms depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common symptoms associated with arm:
- Difficulty gripping or holding objects
- Muscle cramping or twitching
- Numbness or tingling in the arms
- Decreased range of motion
- Muscle atrophy (loss of muscle mass)
- Pain or discomfort in the arms or shoulders
- Difficulty with activities of daily living (ADLs)
- Coordination and balance issues
- Slurred speech (in cases of neurological disorders)

If you experience any of these symptoms along with crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosing Arm Weakness
To determine the underlying cause of weakness, your
ealthcare provider will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, their onset, and any potential triggers or risk factors. They will also perform a physical examination to assess your muscle strength, reflexes, and overall neurological function.
- Imaging Tests: Depending on your symptoms and suspected causes, your doctor may order imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to visualize the affected areas and rule out potential structural abnormalities or injuries.
- Neurological Tests: If a neurological disorder is suspected, your doctor may order tests such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies to evaluate the function of your nerves and muscles.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify underlying conditions, such as vitamin deficiencies, electrolyte imbalances, or autoimmune disorders, that may contribute to arm weakness.
- Cardiac Evaluation: In cases where cardiovascular issues are suspected, your doctor may recommend tests like an electrocardiogram (ECG) or stress test to assess your heart health.
By undergoing a comprehensive evaluation, your healthcare provider can accurately diagnose the cause of your weakness and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatments for Arm Weakness
The treatment approach for arm weakness will depend on the underlying cause and severity of your condition. Here are some potential treatment options:
- Medications:
- Pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs for conditions like arthritis
- Corticosteroids or disease-modifying drugs for autoimmune disorders
- Antiseizure medications for neurological conditions like multiple sclerosis
- Blood thinners or cholesterol-lowering medications for cardiovascular issues
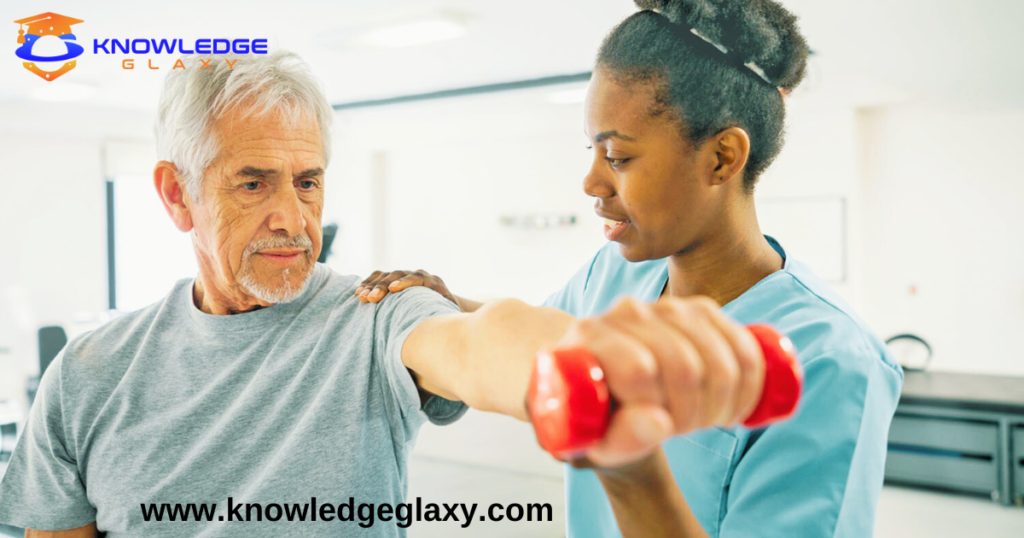
- Physical Therapy and Exercise:
- Strengthening exercises to improve muscle strength and flexibility
- Range-of-motion exercises to maintain mobility
- Occupational therapy to improve daily functioning and independence
- Assistive Devices:
- Braces, splints, or slings to support and stabilize the affected arm
- Mobility aids, such as canes or walkers, to improve balance and prevent falls
- Surgery:
- Procedures to repair damaged muscles, tendons, or nerves
- Joint replacements for severe arthritis
- Decompression surgery for pinched nerves or spinal cord compression
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Ergonomic adjustments to workstations or daily activities
- Weight management to reduce strain on muscles and joints
- Stress management techniques to address emotional factors contributing to arm weakness
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare team, including your primary care physician, physical therapist, and any relevant specialists, to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and preferences.
Prevention and Self-Care Strategies
While some causes of arm weakness may be unavoidable, there are several steps you can take to help prevent or manage arm weakness:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
- Exercise regularly to maintain muscle strength and flexibility
- Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support overall health
- Stay hydrated and manage stress levels
- Practice Good Posture and Ergonomics:
- Maintain proper posture when sitting, standing, or performing activities
- Adjust workstations and equipment to minimize strain on your arms
- Warm Up and Cool Down:
- Before engaging in physical activities, warm up your muscles to prevent injury
- After exercise or strenuous activities, cool down and stretch to reduce muscle fatigue
- Manage Underlying Conditions:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for managing chronic conditions that may contribute to arm weakness, such as diabetes, arthritis, or cardiovascular disease
- Stay Vigilant for Symptoms:
- Be aware of any changes in your arm strength, sensation, or mobility
- Seek prompt medical attention if you experience sudden or worsening arm weakness
By incorporating these preventive measures and self-care strategies into your daily routine, you can potentially reduce your risk of developing arm weakness or manage existing symptoms more effectively.
The Role of Knowledge Galaxy
At Knowledge Galaxy, we understand the importance of providing accurate and accessible information to empower individuals in their journey towards better health and well-being. Our dedicated team of healthcare professionals and researchers is committed to delivering comprehensive resources on various health topics, including.
Through our website, you’ll find in-depth articles, expert insights, and practical advice to help you navigate the challenges of arm weakness. Whether you’re seeking information on potential causes, treatment options, or preventive strategies, Knowledge Galaxy is your trusted source for reliable and easy-to-understand content.
We believe that knowledge is the key to taking control of your health, and our mission is to equip you with the tools and information necessary to make informed decisions. By fostering a supportive and inclusive community, we strive to create a space where individuals can share their experiences, ask questions, and find solace in knowing they are not alone.
Join us at Knowledge Galaxy as we embark on a journey towards understanding and discovering effective solutions to improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Arm weakness can be a concerning symptom with various potential causes, ranging from musculoskeletal conditions to neurological disorders and cardiovascular issues. By recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention, you can receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Read More: Arm Weakness
FAQS
Q1: What are the most common causes of arm weakness?
The most common causes of arm weakness include:
- Stroke: A stroke can cause arm weakness or paralysis, depending on the area of the brain affected.
- Pinched nerve: Compression or irritation of a nerve in the neck or shoulder can lead to arm weakness.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves, often due to diabetes or other conditions, can cause arm weakness.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis in the shoulder or elbow joints can make it difficult to move the arms.
- Injury: Trauma or injury to the muscles, bones, or nerves in the arm can result in weakness.
Q2: Can arm weakness be a sign of a heart attack?
Yes, arm weakness, especially in the left arm, can be a potential sign of a heart attack. This is because a heart attack may cause pain or discomfort that radiates down the left arm, leading to a feeling of weakness or heaviness. If you experience arm weakness accompanied by chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, or other heart attack symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Q3: Is sudden arm weakness a medical emergency?
Sudden arm weakness, especially if it affects only one arm, can be a sign of a stroke or other neurological emergency. In such cases, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention, as prompt treatment can help minimize the potential long-term effects of a stroke or other serious condition.
Q4: How is arm weakness diagnosed?
Arm weakness is typically diagnosed through a combination of methods, including:
- Medical history and physical examination: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, onset, and any potential risk factors or underlying conditions.
- Neurological tests: Tests like electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies can help evaluate nerve and muscle function.
- Imaging tests: MRI, CT scans, or X-rays may be ordered to visualize the affected area and identify any structural abnormalities.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help rule out or confirm certain conditions that may contribute to arm weakness.
Q5: Can arm weakness be a temporary condition?
In some cases, arm weakness can be temporary and resolve on its own or with appropriate treatment. For example, arm weakness caused by a pinched nerve may improve once the nerve compression is relieved. However, in other cases, such as neurological disorders or chronic conditions, arm weakness may be a persistent or recurring issue that requires ongoing management.
Q6: Can physical therapy help with arm weakness?
Yes, physical therapy can be an effective treatment option for arm weakness. A physical therapist can design an exercise program tailored to your specific needs, focusing on strengthening the affected arm muscles, improving range of motion, and enhancing overall functional ability. Occupational therapy may also be recommended to help you adapt to daily activities and regain independence.
Q7: Are there any preventive measures for arm weakness?
While some causes of arm weakness may be unavoidable, there are preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk, such as:
- Maintaining good posture and ergonomics to avoid nerve compression or repetitive strain injuries.
- Exercising regularly to build and maintain arm strength and flexibility.
- Managing underlying conditions like diabetes, arthritis, or cardiovascular disease through lifestyle changes and proper medical treatment.
- Avoiding activities that put excessive strain on your arms, especially if you have an existing injury or condition.
Q8: When should I seek medical attention for arm weakness?
You should seek medical attention for arm weakness if:
- The weakness is sudden or severe.
- The weakness is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, or pain.
- The weakness interferes with your ability to perform daily activities or impacts your quality of life.
- The weakness persists or worsens over time, despite rest and self-care measures.