Introduction
The human brain is the command center of the body, controlling our thoughts, movements, emotions, behaviors, and memories. One of the Structure of Human Brain and Function most complex biological structures in the known universe, the brain contains billions of interconnected neurons and glial cells that communicate through synapses and neural networks. Scientists continue unravelling the mysteries of how this three-pound organ gives rise to human consciousness and cognitive abilities.
Read More: Human Brain Structure

In this article, we’ll explore the major structures and functions of the human brain and nervous system. We’ll examine how neurons communicate, how the brain develops, and some of the imaging techniques allowing neuroscientists to map the brain’s connectivity. Although many questions remain unanswered, unlocking the secrets of the brain promises to transform our understanding of ourselves.
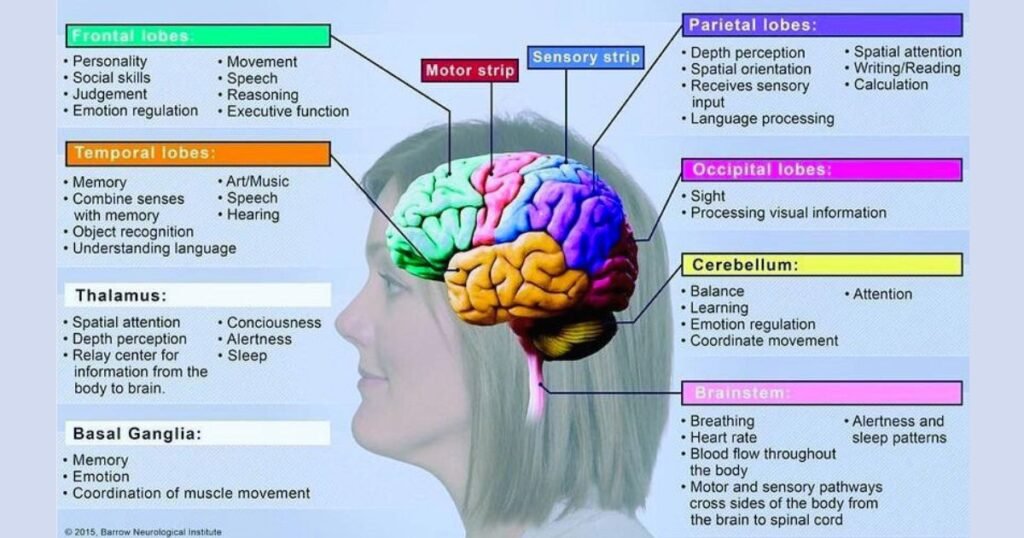
Key Structures and Functions
The human brain can be divided into main structures based on location and function:
- Cerebrum – The largest part of the brain, containing lobes for complex functions like reasoning, emotions, and memory.
- Cerebellum – Located at the base of brain, key for balance, coordination, and motor control.
- Brainstem – Joins the brain and spinal cord, controls Structure of Human Brain and Function essential involuntary functions like breathing.
- Limbic system – Buried inside the cerebrum, drives emotions, behavior, motivation, and long-term memory.
- Cortical layers – The cerebrum has an outer cortex with gray matter and inner white matter connected by axons. Different regions process sensations, thoughts, memories, speech, movements and other complex functions.
Neurons and Neural Transmission
The brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons connected by trillions of synapses. Neurons communicate through electrical and chemical signals. Structure of Human Brain and Function When a neuron fires, it releases neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin into the synapse. The neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the next neuron, stimulating or inhibiting firing.
This neural transmission allows all brain functions – from detecting touch to forming memories. Glial cells support and protect neurons.
Brain Development

The brain starts forming just weeks after conception. Notable milestones include:
- 3 weeks – Neural tube forms, precursor to central nervous Structure of Human Brain and Function system.
- 8 weeks – Brain divided into five regions including cerebrum and cerebellum.
- 5 months – Billions of neurons formed.
- 9 months – Cortex contains most neurons it will ever have. Gray matter thickest.
- 2 years – White matter expands as myelination of axons progresses.
- Puberty – Synaptic pruning refines neural connections. Gray matter thins.
- 25 years – Brain reaches full maturity as prefrontal cortex completes myelination.
Structure of Human Brain and Function
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. It consists of many different regions that perform different functions. These functions include sensory input, motor output, short-term memory, language, and problem solving. Structure of Human Brain and Function Each region of the brain is designed to perform specific functions and it is also designed to connect to other regions of the brain in a specific manner.
Brain Imaging Techniques
Mapping the living, working brain is challenging. Key techniques include:
- fMRI – Detects blood flow to activated brain areas.
- PET – Visualizes glucose metabolism and neurotransmitter activity.
- EEG – Records electrical signals via electrodes on the scalp.
- CT and MRI – X-rays and magnetism provide anatomical brain images.
These technologies allow non-invasive study of brain structure, function, and connectivity.
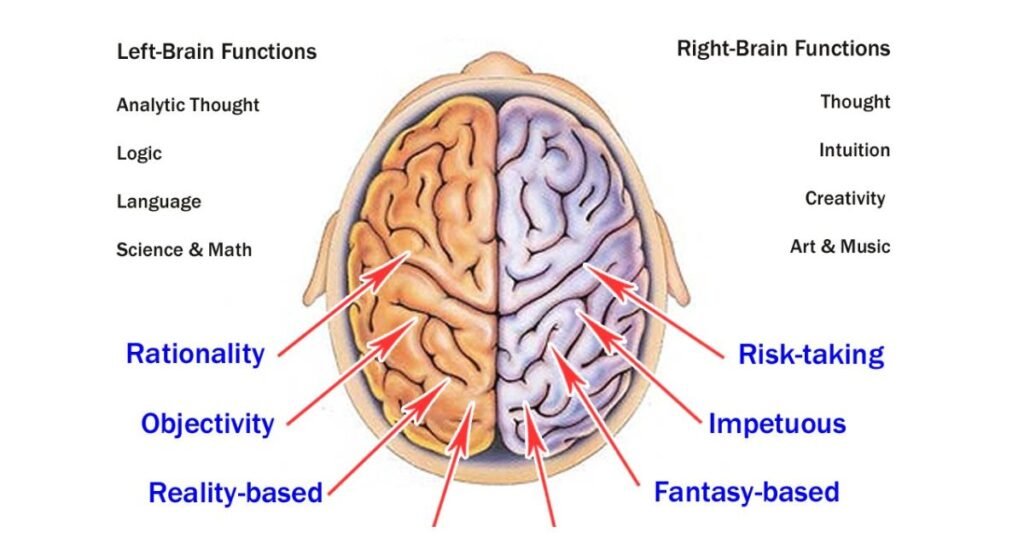
Read More: Structure of Human Brain and Function
Conclusion
The intricacies of the human brain continue intriguing both scientists and philosophers. Discoveries over the past century have uncovered neurons, neurotransmitters, specific functional regions and more, yet exactly how this web of billions of Structure of Human Brain and Function cells generates thought and consciousness remains unknown. As neuroscience and imaging techniques advance, we move closer to illuminating the workings of our most enigmatic organ.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How many neurons are contained in the human brain?
A: The human brain contains roughly 86 billion neurons that are interconnected through trillions of synapses.
Q: Which neural transmitter is associated with pleasure and mood?
A: Dopamine is strongly associated with reward, pleasure, and mood regulation in the brain.
Q: Which part of the brain is most associated with memory?
A: The Structure of Human Brain and Function hippocampus located in the limbic system of the brain plays a crucial role in the formation of memories.
Q: Which imaging technique directly measures brain activity?
A: fMRI detects changes in blood flow Structure of Human Brain and Function in the brain occurring due to neural activity, providing insights into brain function.
Q: At what age is brain development complete?

A: Brain development continues through adolescence and into the mid-20s, with the prefrontal cortex Structure of Human Brain and Function finalizing myelination around 25 years old.