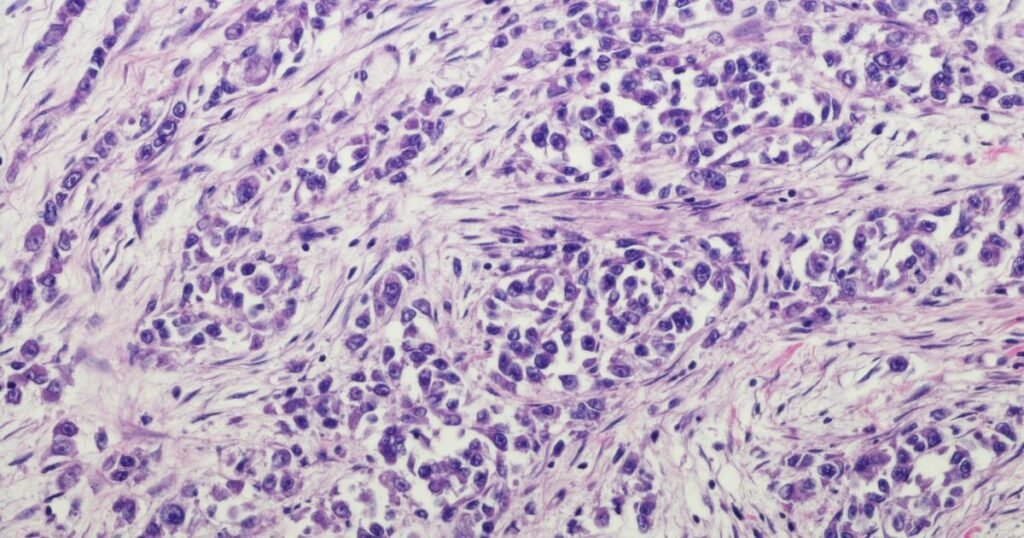
Introduction to Spindle Cell Sarcoma
Spindle Cell Sarcoma is a rare and aggressive type of cancer that originates in the connective tissues of the body. This malignant tumor is characterized by spindle-shaped cells called “spindle cells.”
While spindle cell sarcoma can develop in various parts of the body, it is most commonly found in the limbs, particularly the legs. It can also occur in the trunk, head, neck, and internal organs.
The exact causes of spindle cell sarcoma are still not fully understood. However, certain risk factors have been identified, such as genetic predisposition, exposure to radiation, and previous history of cancer treatment with radiation therapy.
Symptoms of spindle cell sarcoma can vary depending on the location and stage of the tumor. In the early stages, patients may experience pain, inflammaton, or a kind of lump at the tumor site. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include limited range of motion, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, and even difficulty breathing if the tumor affects internal organs.
Diagnosing spindle cell sarcoma involves a series of tests, including imaging scans, biopsies, and pathological examination of the tumor cells
Treatment options for spindle cell sarcoma typically involve a multidisciplinary approach, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The specific treatment regimen depends on various factors, such as the size and location of the tumor, the cancer stage, and the patient’s overall health.
Read More : Kidney Cancer Symptoms
Understanding the causes and risk factors of Spindle Cell Sarcoma
Spindle Cells Sarcoma is a rare form of cancer that develops in the body’s soft tissues. Although the exact reason for the disease is still unknown, medical experts have identified that There are some risk factors that could make Spindle Cell Sarcoma more likely to occur.

Radation Exposure: One of the main risk factors is radiation exposure. Individuals who have previously undergone radiation therapy, either for cancer treatment or diagnostic purposes, may be at a higher risk of developing this type of sarcoma.
Genetic disorders: Additionally, individuals with a history of certain genetic disorders, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome or neurofibromatosis, may also have an increased risk.
It is important to note that while these risk factors can enhance the development of Spindle Cell Sarcoma, but they do not guarantee its occurrence. Many individuals with no known risk factors have also been diagnosed with this condition, highlighting the complex nature of its development.
Researchers continuously study the causes and risk factors associated with Spindle Cell Sarcoma to gain a deeper understanding of its origins. By identifying these factors, medical professionals can offer better guidance and prevention strategies to individuals at a higher risk.
Common symptoms and signs of Spindle Cell Sarcoma
Spindle cell sarcoma is characterized by the growth of abnormal spindle-shaped cells. While this type of cancer can occur in various body parts, it is commonly found in the extremities, such as the arms or legs.
Noticeable Lump: One of the common symptoms is the development of a noticeable lump or mass in the affected area. This lump may be painless initially, but it can become painful and tender to touch as the cancer progresses. It is essential to be vigilant and consult with the health care professional in case of any noticeable changes in the body.

Persistent Pain: Another symptom to watch out for is persistent pain in the affected area. Spindle Cell Sarcoma can cause discomfort or aching that doesn’t subside with time or conventional pain relief methods.
Additionally, as the tumor grows, it may exert pressure on surrounding tissues, nerves, or blood vessels, leading to various symptoms. These can include numbness, tingling sensations, or weakness in the affected limb. If you notice any sensory or motor changes, it is crucial to bring it to the attention of your doctor.
In some cases, Spindle Cell Sarcoma can also cause symptoms such as fatigue, unintentional weight loss, or a general feeling of malaise. These systemic symptoms are not exclusive to this type of cancer and can be present in other conditions. Nevertheless, if you experience these and other concerning signs, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
Diagnostic Procedures for Spindle Cell Sarcoma
When diagnosing spindle cell sarcoma, healthcare professionals will typically employ various diagnostic procedures to accurately identify the condition’s presence and extent. These procedures are crucial in determining the most appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is one of the first steps in the diagnostic process. During this examination, a healthcare provider will carefully assess the affected area or areas, looking for any noticeable abnormalities or signs of spindle cell sarcoma. They may also inquire about the patient’s medical history and any related symptoms they may have been experiencing.
Imaging tests are often utilized following the physical examination to provide a more detailed view of the affected area. Standard imaging techniques used to diagnose spindle cell sarcoma include X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans. These imaging tests can help identify the tumor’s location, size, and spread, aiding in the development of an effective treatment plan.
Biopsy: Once imaging tests have been conducted, a biopsy is usually performed to confirm the diagnosis of spindle cell sarcoma. Durring biopsy, small sample of calls is removed from the affetced area, which is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist. This examination allows for a definitive diagnosis of spindle cell sarcoma. It can also provide valuable information about the specific characteristics of the tumor.
Additional Laboratory Tests: In some cases, additional laboratory tests may be conducted to analyze the tumor further. These tests can include immunohistochemistry, which helps determine the specific types of cells present in cancer, and molecular testing, which can identify specific genetic alterations that may inform treatment decisions.

Different types and stages of Spindle Cell Sarcoma
Spindle cell sarcoma has an elongated and have a unique appearance under the microscope. Although spindle cell sarcoma can occur in various parts of the body, it most commonly affects the limbs, specifically the arms and legs.
There are several different types of spindle cell sarcoma, each with distinct characteristics and behaviors. These include
- undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma,
- fibrosarcoma,
- leiomyosarcoma,
- myxofibrosarcoma
Each class has specific symptoms and treatment options, making an accurate diagnosis crucial for determining the best action.
In addition to different types, spindle cell sarcoma can also be classified into various stages, which helps assess the extent of the disease and plan appropriate treatment strategies. The staging system commonly depends upon about the size of tumor, its invasiveness, and its spreadness to the connected lymph nodes or other organs of the body. Staging helps oncologists determine the most effective treatment plan and prognosis for patients.
Early-stage spindle cell sarcoma may be localized and confined to a specific area, making it more treatable and potentially curable. As the disease progresses to advanced stages, it may spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or distant organs, making treatment more challenging and the prognosis less favorable.
Treatment Options for Spindle Cell Sarcoma
When it comes to treating spindle cell sarcoma, various options are available depending on the stage and location of the tumor. Treatment plans are typically personalized to each individual, taking into consideration factors such as the size and grade of the cancer and the overall health of the patient.
Surgery is often the primary treatment for spindle cell sarcoma. Surgery aims to remove the tumor and any surrounding tissue that may be affected. In some cases, this may involve the removal of a portion of a limb or organ to ensure complete tumor removal. The surgeon will aim to achieve clear margins, which means removing all cancerous cells to minimize the chance of recurrence.
Radiation therapy is another standard treatment option for spindle cell sarcoma. This involves using high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be applied both before and after surgery to either reduce the tumor and make it easier to remove or to further remove any cancer cells that may still be present after surgery.
Chemotherapy, which involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells, is sometimes used in the treatment of spindle cell sarcoma. However, it is less commonly used than surgery or radiation therapy. Patients with advanced or metastatic sarcoma or when surgery cannot entirely remove the tumor may be advised to undergo chemotherapy. It can be given orally or intravenously.
Targeted therapy is a newer approach to treating spindle cell sarcoma. This involves using drugs that specifically target specific molecules or genetic mutations within cancer cells. By targeting these specific abnormalities, targeted therapy aims to halt the progression and its invasiveness to minimize the damage to normal cells. Targeted therapy may be used alone or in combination with other treatment modalities.
Clinical trials may also be an option for patients with spindle cell sarcoma. These trials evaluate new treatment approaches or combinations of existing therapies to determine their effectiveness. Participating in a clinical trial can provide access to cutting-edge treatments that may not be available otherwise.
Surgery
One of the main forms of treatment for spindle cell sarcoma is surgery. Surgery tries to eliminate the tumor and any potentially damaged surrounding tissue. The location and size of the malignancy will determine the kind of surgery needed.
In some cases, a wide local excision may be performed, removing the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue around it. This is often the preferred approach when the tumor is small and localized. The surgeon will aim to achieve clear margins, meaning no cancer cells are detected at the edges of the removed tissue.
A radical resection may be necessary in more advanced cases or when the tumor is located in a difficult-to-reach area. This involves removing a significant portion of tissue, including nearby muscles, bones, or organs. The extent of the surgery will vary depending on the specific circumstances and the surgical team’s expertise.
Depending on the complexity of the procedure and individual conditions, recovery after surgery will vary. Patients frequently report some soreness, edema, and restricted motion in the affected area. To aid with recovery and regain functionality, physical therapy may be advised.
Regular monitoring and surveillance are crucial to detect any signs of recurrence or complications.
Radiation therapy
High-energy radiation beams are used in this treatment to pinpoint and eliminate cancer cells in the affected area.
One of the primary goals of radiation therapy is to shrink tumors and prevent the spread of cancer cells. It can be used either alone or in conjunction with other therapies, like surgery or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and location of the sarcoma.
During radiation therapy, a radiation oncologist carefully plans the treatment to ensure that the tumor receives a precise and effective dose of radiation while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. The treatment is typically delivered in multiple sessions over several weeks, allowing the body time to recover between treatments.
The side effects of radiation therapy for spindle cell sarcoma can vary depending on the location of the tumor and the dosage of radiation used. Common side effects may include fatigue, skin changes in the treated area, and temporary hair loss. These side effects are usually temporary and diminish over time after the completion of the treatment.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a widely used treatment option for spindle cell sarcoma. It involves using powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells and prevent their growth and spread. This treatment approach is particularly practical for sarcomas that have spread to other body parts or cannot be surgically removed.
Chemotherapy medications are frequently given intravenously or orally, which let them to enter the bloodstream and reach cancer cells all over the body.
The goal of chemotherapy in treating spindle cell sarcoma is to shrink tumors, alleviate symptoms, and prolong survival. It may be combined with other treatment modalities, such as surgery or radiation therapy, to maximize its effectiveness.
While chemotherapy can effectively kill cancer cells, it can also have some potential negative effects on the surronding healthy cells of the body which may include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, constant fatigue and a weakened immune system. However, advances in supportive care have significantly improved the management of these side effects, allowing patients to tolerate treatment better.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a specialized approach to treating spindle cell sarcoma that focuses on attacking specific molecules or proteins responsible for the growth and spread of cancer cells. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which affects healthy and cancerous cells, targeted therapy aims to minimize damage to healthy tissues and reduce side effects.
The effectiveness of targeted therapy lies in its ability to disrupt the signaling pathways that drive the growth and survival of spindle cell sarcoma cells. By precisely targeting these specific molecules, targeted therapy can halt the progrpotentially shrink tumors.
One common targeted therapy used in treating spindle cell sarcoma is tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs block the action of specific proteins, known as tyrosine kinases, which play a critical role in promoting cell growth and division. TKIs can inhibit the growth and spread of spindle cell sarcoma cells by inhibiting these proteins.
Another targeted therapy option is immunotherapy, which harnesses the immune system of the body to identify and attack on the abnormal cells. Immunotherapy drugs, such as checkpoint inhibitors, help to remove the “brakes” that prevent immune cells from recognizing and attacking cancer cells. This approach can boost the immune response against spindle cell sarcoma and enhance the body’s ability to fight the disease.
While targeted therapy has shown promise in treating spindle cell sarcoma, it is still an evolving field of research. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring new targeted therapy options and combinations to improve patient outcomes further.
Integrative and complementary therapies for Spindle Cell Sarcoma
When treating Spindle Cell Sarcoma, a rare and aggressive form of cancer, conventional medical treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy play a crucial role.
Integrative therapies focus on combining conventional medicine with evidence-based complementary approaches to support the overall well-being of the patient. These therapies include acupuncture, massage therapy, meditation, yoga, and nutritional counseling. They aim to address the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the patient’s health, providing a holistic approach to their treatment.
Acupuncture, for instance, involves the insertion of thin needles on the specific parts of the body encourage healing by promoting energy flow. It has been found to help manage pain, reduce the side effects of conventional treatments, and enhance cancer sufferers’ overall quality of life.
Massage therapy, on the other hand, can help alleviate muscle tension, reduce anxiety and stress, and improve circulation. It provides a soothing and relaxing experience for patients undergoing intense medical treatments, offering comfort and relief.
Mind-body practices like meditation and yoga have shown promising results in reducing stress, enhancing emotional well-being, and improving the body’s natural healing abilities. These practices focus on mindfulness, breathing techniques, and gentle movements, allowing patients to find inner peace and cope with the challenges of their condition.
Additionally, nutritional counseling is vital in supporting the immune system and optimizing overall health. A nutrients rich diet help strengthen the body’s defenses and enhance the effectiveness of conventional treatments.
It’s important to note that integrative and complementary therapies should always be used in conjunction with conventional medical treatments and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Each patient’s case is unique, and a personalized approach is necessary to ensure the best possible outcomes.
While further research is needed to fully understand the efficacy of these therapies in treating Spindle Cell Sarcoma, they offer a potential avenue for improving the overall well-being of patients and enhancing their treatment experience
Managing the side effects of treatment
When it comes to managing the side effects of treatment for spindle cell sarcoma, it is crucial to have a comprehensive plan in place. The goal is to minimize discomfort and maintain the patient’s best possible quality of life throughout their treatment journey.
One of the most common side effects of treatment is fatigue. Patients need to listen to their bodies and rest when needed. Doing gentle exercises like walking or yoga can also help improve energy levels.
Nausea and vomiting are also common side effects, particularly after chemotherapy sessions. Medications known as antiemetics can be prescribed to help manage these symptoms. Patients should eat small, frequent meals and avoid spicy or greasy foods, which can exacerbate nausea.
Hair loss is another side effect that many patients may experience. This can have a significant impact on self-esteem and body image. Exploring options like wigs, scarves, or hats can provide a sense of normalcy and help boost confidence during this challenging time.
Lastly, emotional support is vital in managing the side effects of treatment. Dealing with a diagnosis of spindle cell sarcoma can be emotionally taxing, and patients may experience anxiety, depression, or feelings of isolation. Seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or engaging in therapy can provide a much-needed outlet for emotional support.
Support and resources for patients and their families
A diagnosis of spindle cell sarcoma can be overwhelming and distressing for patients and their families. However, it’s important to remember that you are not alone in this journey. Numerous support systems and resources are available to help you navigate this challenging time.
One of the first steps is to reach out to support groups and organizations specializing in sarcoma. These groups provide a valuable network of individuals with firsthand experience with spindle cell sarcoma. They can offer guidance, empathy, and encouragement. They can also connect you with other patients and families going through similar situations, providing a sense of community and understanding.
In addition to support groups, there are various online forums and discussion boards where patients and their loved ones can share their experiences, ask questions, and seek advice. These platforms serve as virtual support systems, allowing individuals to connect with others regardless of geographical boundaries.
Oncologists, surgeons, and nurses specializing in sarcoma can offer comprehensive information about treatment options, potential side effects, and strategies to manage symptoms. They can also provide referrals to additional services such as counseling, physical therapy, or pain management specialists to ensure holistic care.
Lastly, exploring online resources from reputable organizations and medical institutions is essential. Websites, articles, and publications on sarcoma provide up-to-date information about the disease, treatment advancements, and ongoing research. These tools can enable patients and their families to take an active role in their care and make well-informed decisions.
Promising research and advancements in the treatment of Spindle Cell Sarcoma
In recent years, promising research and advancements in treating spindle cell sarcoma have brought hope to patients and their families
One area of research that shows promise is targeted therapy. This approach involves identifying specific genetic mutations or alterations in the tumor cells and developing drugs targeting those abnormalities. By targeting the specific genetic drivers of spindle cell sarcoma, targeted therapies have the potential to be more effective and less toxic than traditional chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy is another area of advancement in the field of cancer treatment that holds promise for patients with spindle cell sarcoma. This approach harnesses the power of the immune system to recognize and eliminate cancer cells. Immunotherapy drugs, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, have shown encouraging results in treating various types of cancer, including those with spindle cell sarcoma.
Furthermore, surgical techniques and radiation therapy advancements have improved patient outcomes with spindle cell sarcoma. Surgeons can now perform more precise and targeted surgeries, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues while effectively removing the tumor. Radiation therapy like IMRT (Intensity-modulated radiation therapy allow for more accurate radiation delivery to the tumor site, reducing side effects and improving treatment outcomes.
Clinical trials also play a crucial role in advancing the treatment options for spindle cell sarcoma. These trials evaluate new drugs, treatment approaches, and combinations of therapies to improve patient outcomes. Participating in clinical trials provides access to cutting-edge treatments. It contributes to the overall understanding of the disease, leading to further advancements in the field.
We hope this article on understanding spindle cell sarcoma has provided valuable information about this rare form of cancer. By highlighting the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we aimed to raise awareness and provide support for those affected by this condition. Early detection and proper medical care are crucial in managing spindle cell sarcoma.