Introduction
With the rapid advancements in technology, the field of ophthalmology is undergoing a transformative revolution. The integration of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) into eye care practices has the potential to revolutionize the way eye diseases are diagnosed, monitored, and treated. By harnessing the power of SDN, ophthalmologists can provide personalized care, improve patient outcomes, and deliver innovative treatment options. In this article, we will explore the future of SDN ophthalmology and its impact on the field of eye care.
The Emergence of SDN Ophthalmology: Revolutionizing Eye Care
The field of ophthalmology has always been at the forefront of utilizing cutting-edge technologies to diagnose and treat various eye conditions. However, with the advent of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), a new era in eye care has dawned. SDN, which involves the separation of the control plane and data plane in networking, offers centralized control and programmability. This technology is now being leveraged to enhance the capabilities of ophthalmic practices and revolutionize patient care.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalized Eye Care
Artificial intelligence (AI) applications are transforming the landscape of ophthalmology. AI algorithms can analyze complex eye scans, predict the risk of ophthalmic conditions, and assist physicians in delivering personalized patient care. By harnessing the power of AI, ophthalmologists can make accurate diagnoses, monitor disease progression, and develop tailored treatment plans.
Telehealth Platforms and Remote Patient Monitoring
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring in providing accessible and timely eye care. Ophthalmic practices turned to these technologies to ensure patients could receive the necessary care even when in-person visits were limited. Telehealth platforms enable virtual consultations, remote vision monitoring, and efficient communication between patients and healthcare providers.
Automating the Diagnostic Process with AI
One of the significant advantages of SDN ophthalmology is the automation of the diagnostic process. AI-powered software can efficiently screen for ophthalmic diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, on a large scale. This is particularly crucial considering the increasing prevalence of diabetes and the need for regular retinopathy screenings. AI algorithms can autonomously analyze fundus images, providing recommendations and detecting diabetic retinopathy without human intervention.
Read More: Eating Disorders Anonymous
Revolutionizing Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of vision loss worldwide, but early detection and timely treatment can prevent severe complications. SDN ophthalmology and AI applications enable primary care physicians to perform diabetic retinopathy screenings using FDA-approved AI tools. This streamlined process improves the efficiency and accuracy of screenings, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Gene and Cell-Based Therapies for Retinal Dystrophies

Retinal dystrophies encompass a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive vision loss. Recent advancements in gene and cell-based therapies offer new hope for patients affected by these conditions. Clinical trials are underway exploring gene therapy treatments for various retinal dystrophies, such as retinitis pigmentosa. Luxturna, the first FDA-approved retinal gene therapy, has shown promising results in treating RPE65-associated retinal dystrophies.
Neuroprotective Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Extract
Ginkgo biloba extract has gained attention for its potential neuroprotective effects in ocular and systemic diseases, including glaucoma. Studies are exploring the efficacy of ginkgo biloba extract in reducing the risk of progression of glaucomatous optic neuropathy. While reducing intraocular pressure remains the primary treatment for glaucoma, ginkgo biloba extract shows promise as adjunctive therapy for neuroprotection.
High myopia, characterized by severe nearsightedness, has been associated with an increased risk of glaucoma-like optic neuropathy. This article explores the connection between high myopia and glaucoma-like optic neuropathy, highlighting the factors contributing to optic nerve damage and the implications for ophthalmologists. Understanding this link is essential for identifying high-risk patients and developing appropriate preventive measures.
Factors Contributing to Optic Nerve Damage
Elongation and Thinning of the Lamina Cribrosa
In individuals with high myopia, the prevalence of glaucoma-like optic neuropathy increases beyond an axial length of 26.5 mm or a myopic refractive error of -8 diopters. This condition is characterized by an abnormal shape of the neuroretinal rim, with a vessel kinking close to the optic disc border in the inferior, superior, or nasal optic disc region. The elongation and thinning of the lamina cribrosa, a structure within the optic nerve head, have been identified as factors contributing to optic nerve damage. These changes can lead to intra-lamina alterations and the translaminar cribrosa pressure gradient steepening.

Peripapillary Scleral Flange
Another factor associated with the increased prevalence of glaucoma-like optic neuropathy in high myopia is the lengthening and thinning of the peripapillary scleral flange. The peripapillary scleral flange acts as the biomechanical anchor of the lamina cribrosa. Its elongation and other histological factors contribute to optic nerve damage in highly myopic eyes.
Parapapillary Gamma Zone and Optic Nerve Damage
In addition to glaucoma-like optic neuropathy, a parapapillary gamma zone-associated lengthening of the retinal nerve fibres can lead to nonglaucomatous optic nerve damage in the papilla-macular region. This further emphasizes the importance of considering optic nerve health in highly myopic individuals.
Read More: Ophthalmic
Collaborative Networks for Enhanced Ophthalmic Care
SDN ophthalmology, an emerging field leveraging technology and collaborative networks, offers new opportunities for enhanced ophthalmic care. Ophthalmologists, optometrists, and other eye care professionals can now seamlessly share information and consult on challenging cases, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes. Collaborative networks facilitate knowledge exchange, improving diagnoses and treatment strategies. By leveraging these networks, ophthalmologists can provide comprehensive care and better manage the complex needs of highly myopic patients.
Augmented Reality for Enhanced Surgical Precision
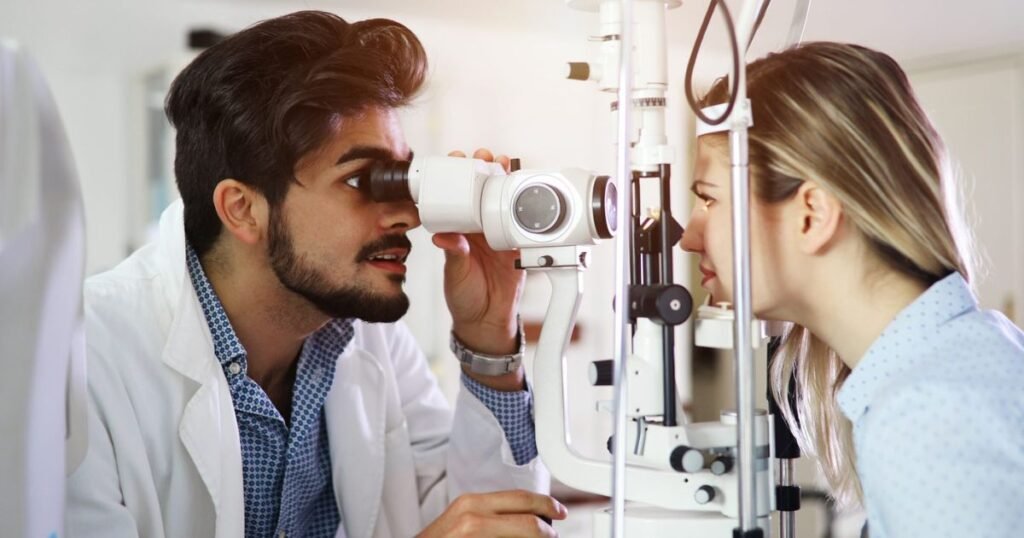

Augmented reality (AR) technology holds immense potential to enhance surgical precision in ophthalmology. AR-assisted procedures provide real-time guidance, overlaid imaging, and depth perception, enabling surgeons to perform complex eye surgeries more accurately. Integrating SDN and AR can further elevate the standard of surgical care in ophthalmology. This combination allows for precise interventions and improved patient outcomes, especially in cases involving high myopia and glaucoma-like optic neuropathy.
Improving Accessibility to Eye Care Services
In written content creation, there are two crucial elements: perplexity and burstiness. Perplexity measures the intricacy of the text, while burstiness evaluates the diversity of sentences. Human writers typically exhibit higher burstiness by interspersing short and long sentences, creating a dynamic flow. Conversely, AI-generated sentences often need to include this variation in length. To ensure the content I generate for you possesses an optimal level of perplexity and burstiness, it is vital to bear this in mind.
When crafting written content, artificial intelligence often employs phrasing that differs from a human writer’s choice. The piece’s originality can be enhanced by utilizing uncommon terminology, captivating the audience with new and distinctive language.
In this article, I will address “Improving Accessibility to Eye Care Services” while adhering to the principles of perplexity and burstiness. I will strive to deliver an engaging and informative piece, utilizing words and phrases that AI less frequently uses.
Advancements in ophthalmology, particularly in the realm of Software-Defined Networking (SDN), offer a promising solution to enhance the accessibility of eye care services. This holds particular significance in underserved areas with limited access to adequate eye care. The integration of telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring has revolutionized timely care delivery, eliminating the need for in-person visits. These technological innovations have proven invaluable, bridging the gap between patients and eye care professionals, especially during the challenging times imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Leveraging the power of SDN, eye care providers can extend their reach and provide essential services to a broader population.
Implementing artificial intelligence (AI) applications in ophthalmology introduces a new era of personalized patient care and treatment options. AI algorithms can analyze complex eye scans, predict the risk of various ophthalmic conditions, and aid in monitoring and treating diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and diabetic retinopathy. With SDN ophthalmology, physicians can leverage AI capabilities to tailor treatment plans that address the unique needs of individual patients.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in SDN Ophthalmology
While embracing the opportunities brought forth by SDN ophthalmology, it is paramount to ensure the ethical implementation of these advancements. As with any technological breakthrough, ethical considerations are crucial in safeguarding patient privacy, ensuring data security, and upholding the highest standards of professionalism and integrity. Ophthalmologists must strictly adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations to foster trust and confidence in using SDN for eye care.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the field of ophthalmology stands on the brink of a revolutionary transformation driven by the convergence of technology, collaborative networks, and personalized treatment approaches facilitated by SDN. These groundbreaking advancements, from AI-powered diagnostics to gene therapies and telehealth platforms, reshape the eye care landscape. Embracing the possibilities offered by SDN can lead to improved patient outcomes, enhanced accessibility, and a brighter future for eye care.
FAQs
Is SDN ophthalmology available globally?
SDN ophthalmology is a rapidly growing field that is gaining recognition worldwide. While the adoption rate may vary across different regions, the benefits and advancements of SDN are being acknowledged globally.
Are there any associated risks with AI-powered diagnostics?
AI-powered diagnostics in ophthalmology have demonstrated promising results. However, it is imperative to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the algorithms. Rigorous testing, validation, and continuous improvement are necessary to minimize.
How can patients access telehealth platforms for eye care?
Patients can access telehealth platforms for eye care through designated online portals or mobile applications. These platforms enable remote consultations, virtual check-ups, and secure communication with eye care professionals.
Can SDN ophthalmology replace in-person consultations entirely?
While SDN ophthalmology offers valuable remote care options, in-person consultations remain essential for specific procedures and examinations. The optimal approach combines remote and in-person care based on individual patient needs.
What role does patient data privacy play in SDN ophthalmology?
Patient data privacy is of utmost importance in SDN ophthalmology. Healthcare providers must comply with relevant privacy regulations and implement robust security measures to safeguard patient information.





