Introduction
The human brain is one of the most remarkably Parts of Human Brain complex biological structures known to science. Weighing just three pounds, this intricate organ controls everything from breathing and heartbeat to personality, memories, and emotions. Composed of billions of interconnected neurons and glial cells, the brain can be divided into main structures based on location and function. By exploring these key parts of the brain, we can better understand how this biological computer gives rise to human cognition and capabilities.
In this article, we’ll tour the major structures of the brain and their roles in generating the extraordinary abilities of the human mind. From the Parts of Human Brain wrinkled cortex that enables rational thought to the limbic system where emotions are processed, discover how the brain’s parts work in synergy to make us human.
Read More: Brain Coronavirus Neurology

The Brain’s Hemispheres and Lobes
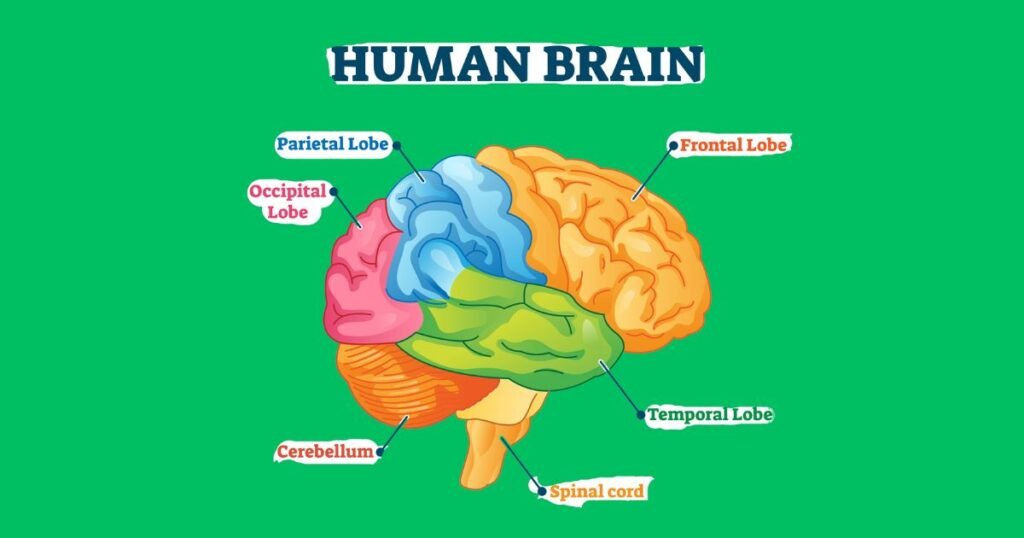
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, accounting for around two-thirds of total brain weight. It is divided into left and right hemispheres and four lobes:
- Frontal – Decision-making, reasoning, parts of speech, movement
- Parietal – Sensory processing, spatial orientation
- Temporal – Memory, sequencing, language comprehension
- Occipital – Visual processing
Deep within the cerebrum lies the limbic system, which regulates emotion, motivation, learning, and memory formation. The hippocampus and amygdala Parts of Human Brain are key limbic structures.
The cerebellum sits below the cerebrum at the base of the brain. It controls coordination and balance.
Parts of Human Brain and Its Functions
The brainstem connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord, forming the central core of the brain. It contains:
- Midbrain – Visual and auditory processing
- Pons – Sleep regulation, arousal
- Medulla – Cardiac, respiratory, and vasomotor centers
The reticular formation running through the brainstem regulates wakefulness and sleep-wake transitions. The brainstem coordinates critical involuntary Parts of Human Brain functions to keep us alive.
Cortex Composition and Neurons

The brain’s cortex has an outer gray matter layer and an inner white matter layer. Gray matter contains neuron cell bodies while white matter consists of axons connecting neurons.
The cerebrum has around 20 billion neurons, the “computational units” of the brain. These connect into complex circuits and pathways that underlie everything from sensory perception to storing memories.
Protective Structures and Fluids The brain needs extensive protection:
- Blood-brain barrier – Tightly controls transport of molecules between blood and brain fluid.
- Meninges – Membranes enclosing the brain and spinal cord. Parts of Human Brain Include the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
- Cerebrospinal fluid – Cushions and protects the brain and spine while also nourishing them.
- Skull – The bony cranium provides structural protection for the soft brain tissue.
Conclusion
While we are still discovering how the interactions between the brain’s structures and cells give rise to thought and consciousness, our exploration of the major parts of the brain provides a glimpse into this remarkable organ. From the essential functions of the brainstem, to the rational capabilities of the cerebrum, the structures of the human brain Parts of Human Brain work in synergy to generate the extraordinary abilities of our species. As neuroscience progresses, so will our understanding of both the anatomical pieces and the emergent whole that makes us human.
Read More: Parts of Human Brain

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Which part of the brain controls memory?
A: The hippocampus located in the limbic system of the brain plays a key role in forming memories.
Q: What part of the brain processes emotions?
A: The limbic system, especially the amygdala, processes emotions and emotional responses.
Q: What does the cerebellum do?
A: The cerebellum regulates coordination, balance, posture, and motor control.
Q: What are the four lobes of the brain?
A: The four lobes are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes located in the cerebrum.
Q: What fluid protects and nourishes the brain?
A: Cerebrospinal fluid cushions the brain, provides nutrients, removes waste, and protects it from infection.