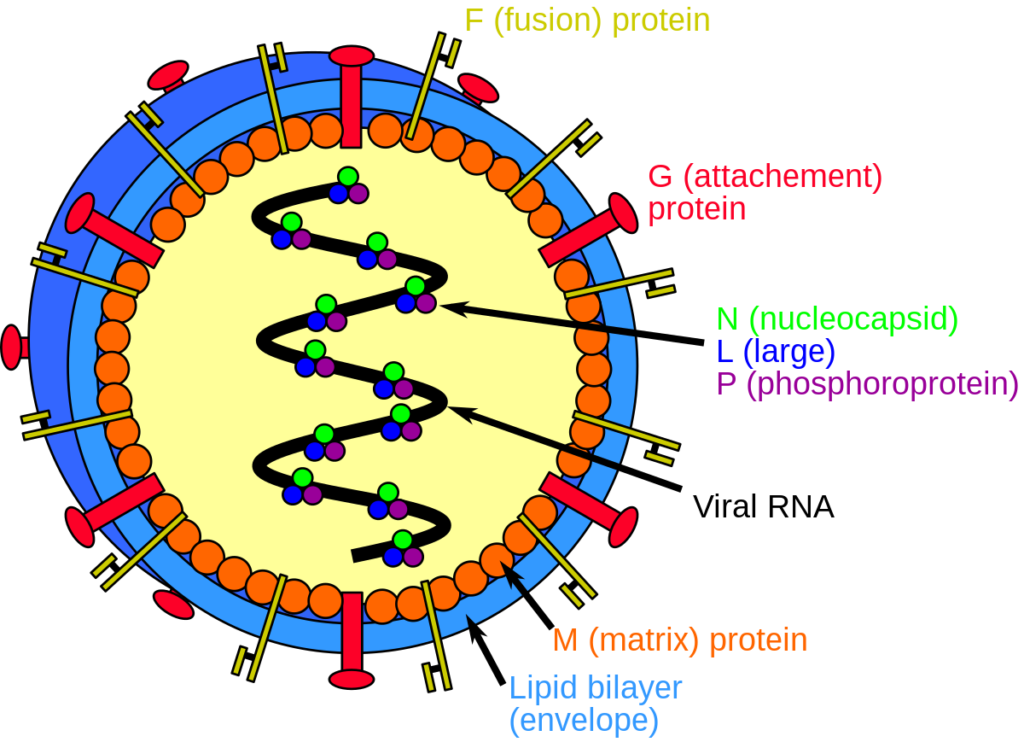
Outline
I. Introduction – Definition of Nipah Virus Infection – Brief history and origin of Nipah Virus
II. Symptoms and Transmission – Common symptoms of Nipah Virus Infection – Modes of transmission
III. Outbreaks and Impact – Notable outbreaks of Nipah Virus Infection – Impact on public health
IV. Prevention and Control – Measures to prevent Nipah Virus Infection – Importance of surveillance and early detection
V. Treatment and Research – Current treatment options – Ongoing research and development efforts
VI. Nipah Virus and Public Health Preparedness – Importance of public health infrastructure – Preparedness strategies for Nipah Virus outbreaks
VII. Conclusion – Recap of key points – Importance of continued research and vigilance
VIII. FAQs 1. What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus Infection? 2. Can Nipah Virus be transmitted from person to person? 3. Are there any vaccines available for Nipah Virus? 4. What should I do if I suspect Nipah Virus infection? 5. How can I protect myself from Nipah Virus?
Nipah Virus Infection
Nipah Virus is a zoonotic virus that causes severe respiratory illness and encephalitis in humans. It was first identified in 1998 during an outbreak in Malaysia and Singapore, and since then, several outbreaks have been reported in different parts of the world. The virus is primarily transmitted from animals to humans, with bats being the natural reservoir. In this article, we will explore the symptoms, transmission, impact, prevention, treatment, and public health preparedness regarding Nipah Virus Infection.
Introduction
Nipah Virus Infection is a zoonotic disease caused by the Nipah Virus (NiV), which belongs to the Paramyxoviridae family. The virus was first identified in 1998 in Malaysia when an outbreak of respiratory illness and encephalitis occurred among pig farmers and those in close contact with pigs. The virus is named after the village in Malaysia where the outbreak originated.
Symptoms and Transmission
The symptoms of Nipah Virus Infection can range from mild to severe. The initial signs include fever, headache, muscle pain, and respiratory symptoms such as cough and sore throat. As the infection progresses, it can lead to encephalitis, characterized by drowsiness, disorientation, and neurological signs. In severe cases, it can result in coma or death.
Nipah Virus is primarily transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals, especially pigs and bats. Consumption of fruits or juices contaminated with bat saliva or urine is another common mode of transmission. In some cases, person-to-person transmission has also been reported, particularly in healthcare settings where proper infection control measures were not implemented.

Outbreaks and Impact
Since its discovery, Nipah Virus has caused several outbreaks in different countries, including Malaysia, Singapore, Bangladesh, and India. These outbreaks have resulted in significant morbidity and mortality, with mortality rates ranging from 40% to 75%. The impact of Nipah Virus Infection goes beyond the immediate health effects, as it can lead to economic losses and disrupt local healthcare systems.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Nipah Virus Infection requires a multi-faceted approach. Some preventive measures include avoiding direct contact with infected animals, practicing good hygiene, and thoroughly washing fruits before consumption. In regions where Nipah Virus outbreaks have occurred, public health authorities implement surveillance systems to detect and respond to cases promptly.
Read More : Olive Oil
Prevention and Control (continued)
Isolation of infected individuals and strict infection control practices are crucial in healthcare settings to prevent person-to-person transmission. Additionally, efforts are made to educate communities about the risks associated with Nipah Virus and promote awareness of preventive measures.

Treatment and Research
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment for Nipah Virus Infection. Supportive care, such as managing symptoms and providing respiratory support, is the mainstay of treatment. However, ongoing research is focused on developing effective antiviral drugs and vaccines to combat the virus.
Scientists and researchers are studying the genetic makeup of the Nipah Virus to better understand its transmission patterns, virulence factors, and potential drug targets. They are also exploring the development of vaccines that can confer immunity against Nipah Virus infection.
Nipah Virus and Public Health Preparedness
Nipah Virus outbreaks serve as a reminder of the importance of robust public health infrastructure and preparedness. Surveillance systems need to be strengthened to detect and respond to outbreaks promptly. Early diagnosis, contact tracing, and isolation of cases are critical in preventing the spread of the virus.
Public health agencies and healthcare facilities should prioritize training healthcare workers in infection control practices to minimize the risk of transmission within healthcare settings. Rapid communication and collaboration between local, national, and international health authorities are vital to coordinate responses and control the spread of the virus during outbreaks.

Read More : Website
Conclusion
Nipah Virus Infection is a serious public health concern due to its high mortality rate and potential for person-to-person transmission. It is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in preventing and controlling outbreaks. Ongoing research and international collaboration are essential in developing effective treatment options and vaccines to mitigate the impact of Nipah Virus.
By implementing robust surveillance systems, promoting awareness, and strengthening public health infrastructure, we can minimize the risk of Nipah Virus outbreaks and protect communities from this deadly infection.
FAQs
- What is the mortality rate of Nipah Virus Infection?
- The mortality rate of Nipah Virus Infection can range from 40% to 75%, depending on the outbreak and healthcare measures in place.
- Can Nipah Virus be transmitted from person to person?
- Yes, person-to-person transmission of Nipah Virus can occur, particularly in healthcare settings or close contact with infected individuals.
- Are there any vaccines available for Nipah Virus?
- Currently, there are no approved vaccines for Nipah Virus, but research is underway to develop effective vaccines.
- What should I do if I suspect Nipah Virus infection?
- If you suspect Nipah Virus infection, seek medical attention immediately and follow the guidance of healthcare professionals. Isolation and infection control measures are crucial.
- How can I protect myself from Nipah Virus?
- To protect yourself from Nipah Virus, avoid direct contact with infected animals, practice good hygiene, wash fruits thoroughly before consumption, and follow any public health advisories or guidelines provided during outbreaks.