Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a progressive autoimmune condition that affects the central nervous system. It damages the protective myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers, causing communication issues between the brain and body. While there is no cure yet, therapies and lifestyle changes can help manage MS symptoms and slow progression.
Read More: Neuroscience
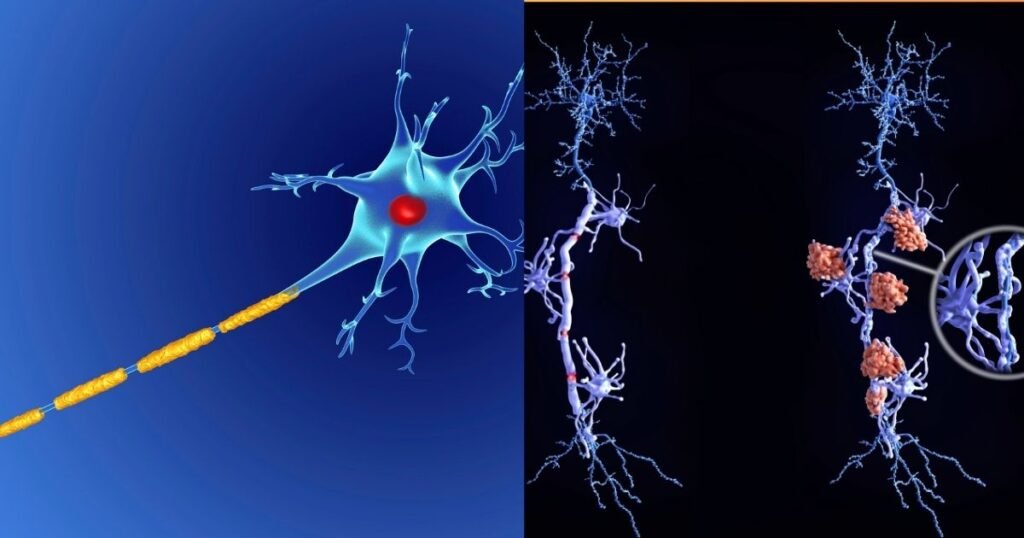
Causes and Pathology
MS is caused by the immune system wrongly attacking the myelin layers insulating nerve cells in the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. This leads to inflammation and scar tissue buildup called lesions or plaques. Over time, this interference disrupts signals traveling along nerve cell axons, resulting in the signs and symptoms of MS.
Multiple Sclerosis
What exactly triggers the abnormal autoimmune response remains unclear. Combinations of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors like low Vitamin D, smoking, and Epstein-Barr Virus are thought to be involved. MS is not directly inherited, but having a family member with it does increase risk.
Types of MS
There are several classifications of MS based on the progression pattern:
- Relapsing-remitting MS: Periods of new or worsening symptoms followed by recovery and remission. Most common form.
- Secondary progressive MS: Steady worsening of symptoms over time after the relapsing-remitting stage.
- Primary progressive MS: Slow but constant decline in function from the outset with no distinct attacks or remissions.
- Progressive-relapsing MS: Steady progression from the start with acute relapses along the way.

Symptoms
Symptoms of MS occur when inflammation and nerve damage disrupt normal neurological function:
- Numbness, tingling, weakness in limbs
- Blurred or double vision
- Slurred speech
- Dizziness, vertigo
- Muscle spasms, stiffness, tremor
- Chronic fatigue
- Walking/balance/coordination problems
- Bladder dysfunction
- Sexual dysfunction
- Cognitive changes
MS flare-ups can produce new symptoms or Multiple Sclerosis exacerbate existing ones. Attack severity and specific manifestations vary person-to-person.
Diagnosis
MS diagnosis involves:
- Medical history and neurological exam to identify characteristic symptoms/signs
- MRI tests showing lesions in particular CNS locations
- Spinal fluid analysis for inflammatory antibodies
- Testing to rule out conditions that mimic MS

There is no single conclusive test for MS. Doctors synthesize tests, exams and presentation to reach a diagnosis. It may take some time to definitively diagnose.
Treatment Approaches
While there is no cure for MS yet, therapies aim to modify disease activity and manage symptoms:
- Corticosteroids reduce inflammation during acute attacks.
- Disease-modifying drugs slow the immune assault on myelin to limit damage and disability progression.
- Muscle relaxants, antidepressants, and pain meds treat specific symptoms.
- Physical therapy preserves mobility, Multiple Sclerosis balance, and coordination.
- Healthy lifestyle habits like exercise, stress reduction, and a anti-inflammatory diet help control MS progression.
Along with traditional approaches, some patients find relief through alternative medicine like massage, meditation, cannabis, and acupuncture. Multidisciplinary care provides the best quality of life.
Outlook
MS symptoms and progression vary widely from person to person based on the areas of the CNS affected. Lifespan is not generally affected, but disability can develop Multiple Sclerosis depending on severity. Living a healthy lifestyle and actively managing MS is key.
While MS itself is not fatal, complications like infections, falls, and secondary effects can become serious. Disability often accumulates over decades, emphasizing the need for early treatment. Research toward better therapies and a cure continues.
Conclusion
MS is a complex autoimmune illness that disrupts nerve signaling in the central nervous system. Cause is not fully understood, but interaction between genes and environment Multiple Sclerosis plays a role. Managing MS through medications, alternative approaches, diet, and lifestyle provides the best odds of preserving function and quality of life.
Read More: Multiple Sclerosis

Relevant FAQs:
Q: Is MS considered a form of dementia?
A: No, MS is not dementia as it does not directly damage neurons or mimic Alzheimer’s disease. However, it can cause cognitive changes over time.
Q: What is an MS hug?
A: An MS hug refers to sensations of tightness, squeezing or pain around the torso caused by nerve dysfunction.
Q: Does MS shorten lifespan?
A: MS is not directly fatal, but complications from advanced disease can impact longevity in some cases. With proper management, normal lifespan is common.
Q: Can you fully recover from an MS attack?
A: Recovery is possible, especially with early treatment. However, each attack can cause some permanent nerve damage that Multiple Sclerosis accrues over time.
Q: Is MS more common in women?

A: Yes, statistics show MS affects over twice as many women as men. The reasons for this disparity are not yet fully understood.






