Dementia is a broad term used to describe a decline in cognitive function severe enough to interfere with daily life. Dementia is not a specific disease, Dementia and Cognition but rather a group of symptoms that can be caused by various underlying conditions. The most common cause of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, but other causes include vascular disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Cognition refers to the mental processes that allow us to think, remember, and learn. In dementia, cognition is severely impaired, leading to memory loss, difficulty with language, disorientation, confusion, and changes in mood and behavior.

Introduction
Dementia is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is important to raise awareness and understanding about dementia cognition to ensure timely detection, intervention, and support for those affected. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of dementia cognition, including its symptoms, causes, and when to seek medical attention.
Read More: Sky King Fireworks
Understanding Dementia
Dementia is a broad term used to describe a range of symptoms that significantly impact memory, thinking, and social abilities. It is not a specific disease itself, Dementia and Cognition but rather a collective term for several diseases that cause these symptoms. Memory loss is one of the common signs of dementia, although it can have various underlying causes.
Causes of Dementia
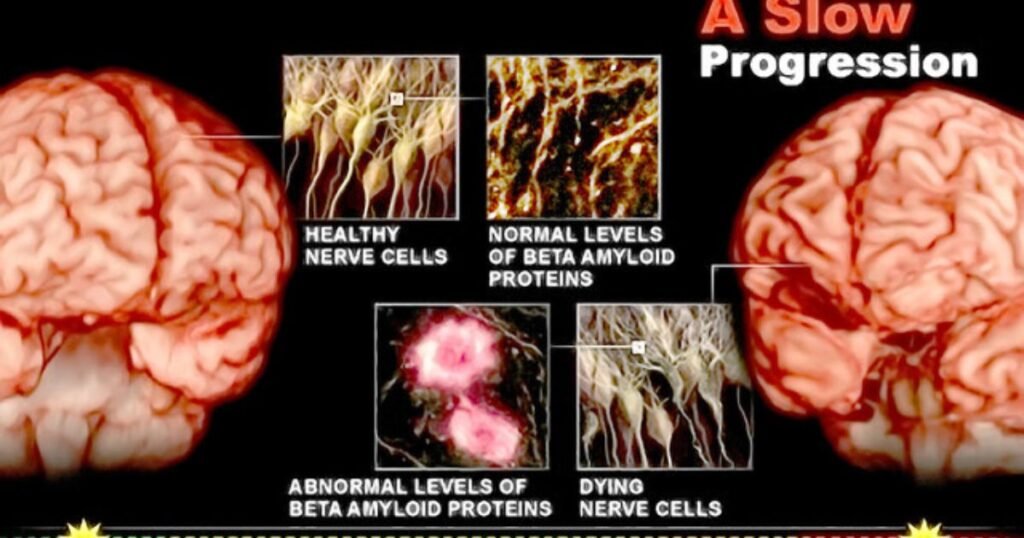
Dementia is primarily caused by damage or loss of nerve cells and their connections in the brain. The specific area of the brain affected determines how dementia Dementia and Cognition manifests and what symptoms are experienced. Dementias are often categorized based on commonalities, such as the protein deposits found in the brain.
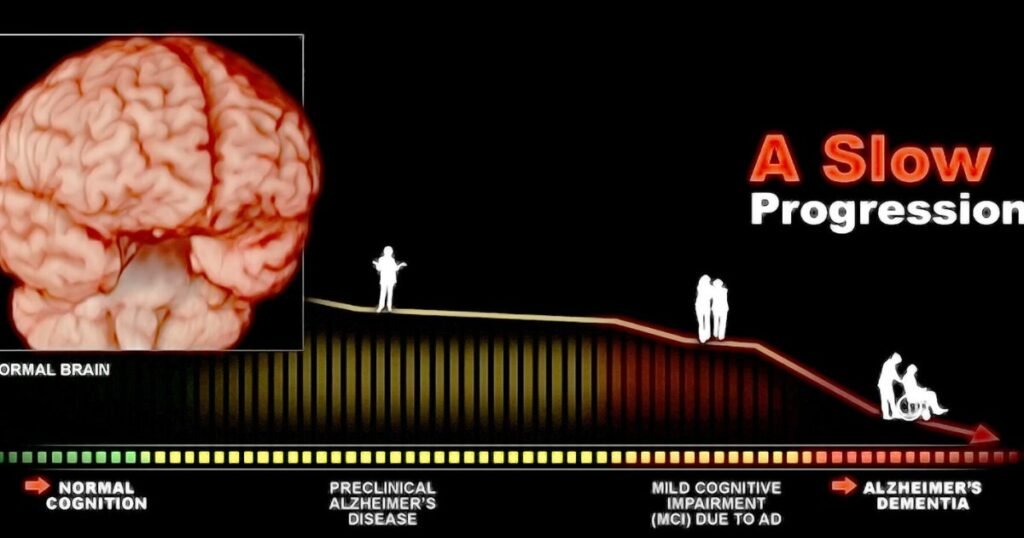
Dementia and Cognitive Impairment
Dementia can lead to various cognitive impairments that significantly impact a person’s daily life. Let’s explore some of the key cognitive changes associated with dementia:
Memory Loss
Memory loss is one of the hallmark symptoms of dementia. It is typically noticed by someone else rather than the affected individual. Memory loss in dementia Dementia and Cognition goes beyond normal age-related forgetfulness and can severely disrupt daily functioning.
Difficulty with Communication and Language
Individuals with dementia often face challenges in finding words, expressing themselves, or understanding others. Difficulty with communication and language can lead to frustration and isolation.
Impaired Visual and Spatial Abilities
Dementia can affect a person’s visual and spatial abilities, Dementia and Cognition making it difficult to perform tasks such as driving or navigating familiar surroundings. Spatial disorientation and getting lost are common symptoms.
Challenges in Reasoning and Problem-Solving
Dementia can impair a person’s ability to reason, solve problems, and make sound judgments. Tasks that require complex thinking and decision-making become increasingly challenging.

Trouble with Planning and Organizing
Individuals with dementia often struggle with planning and organizing tasks. Dementia and Cognition They may find it challenging to create and follow routines or manage multiple steps involved in daily activities.
Coordination and Motor Function Issues
Dementia can affect coordination and motor functions, leading to difficulties with movements, balance, and performing Dementia and Cognition tasks that require fine motor skills.
Confusion and Disorientation
People with dementia often experience confusion and disorientation. They may struggle to recognize familiar places, faces, or even their own belongings. Confusion can cause anxiety and distress.
Psychological Changes
Dementia can bring about various psychological changes, including alterations in personality, depression, anxiety, paranoia, agitation, and even hallucinations. These changes can significantly impact a person’s emotional well-being and interactions.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you or a loved one is experiencing memory problems or other symptoms of dementia, it is crucial to seek medical attention. Early detection and diagnosis can help identify any underlying treatable conditions that may be causing the symptoms. It is important to determine the cause of dementia to provide appropriate care and support.
Read More: Dementia and Cognition
Conclusion
Dementia cognition is a complex topic that encompasses a range of symptoms and challenges faced by individuals affected by dementia. Dementia and Cognition Understanding the signs, causes, and implications of cognitive impairments associated with dementia is crucial for timely intervention, support, and care. If you or someone you know is experiencing memory loss or other dementia symptoms, consult a healthcare professional to determine the cause and explore appropriate treatment options.
FAQs
Is dementia a specific disease?
Dementia is not a specific disease itself but a term used to describe a group of symptoms caused by various underlying diseases.
What are the common symptoms of dementia?
Common symptoms of dementia include memory loss, difficulty with communication, impaired spatial abilities, challenges in reasoning and problem-solving, and psychological changes such as depression and anxiety.
Can dementia be treated or cured?
While there is currently no cure for most types of dementia, certain medications and therapies can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease.
Is memory loss always a sign of dementia?
Memory loss alone does not necessarily indicate dementia. It can be caused by various factors, including normal aging, stress, certain medications, or medical conditions. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
How can dementia be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all types of dementia, adopting a healthy lifestyle, engaging in regular physical and mental activities, maintaining social connections, managing chronic conditions, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can potentially reduce the risk of developing dementia.






